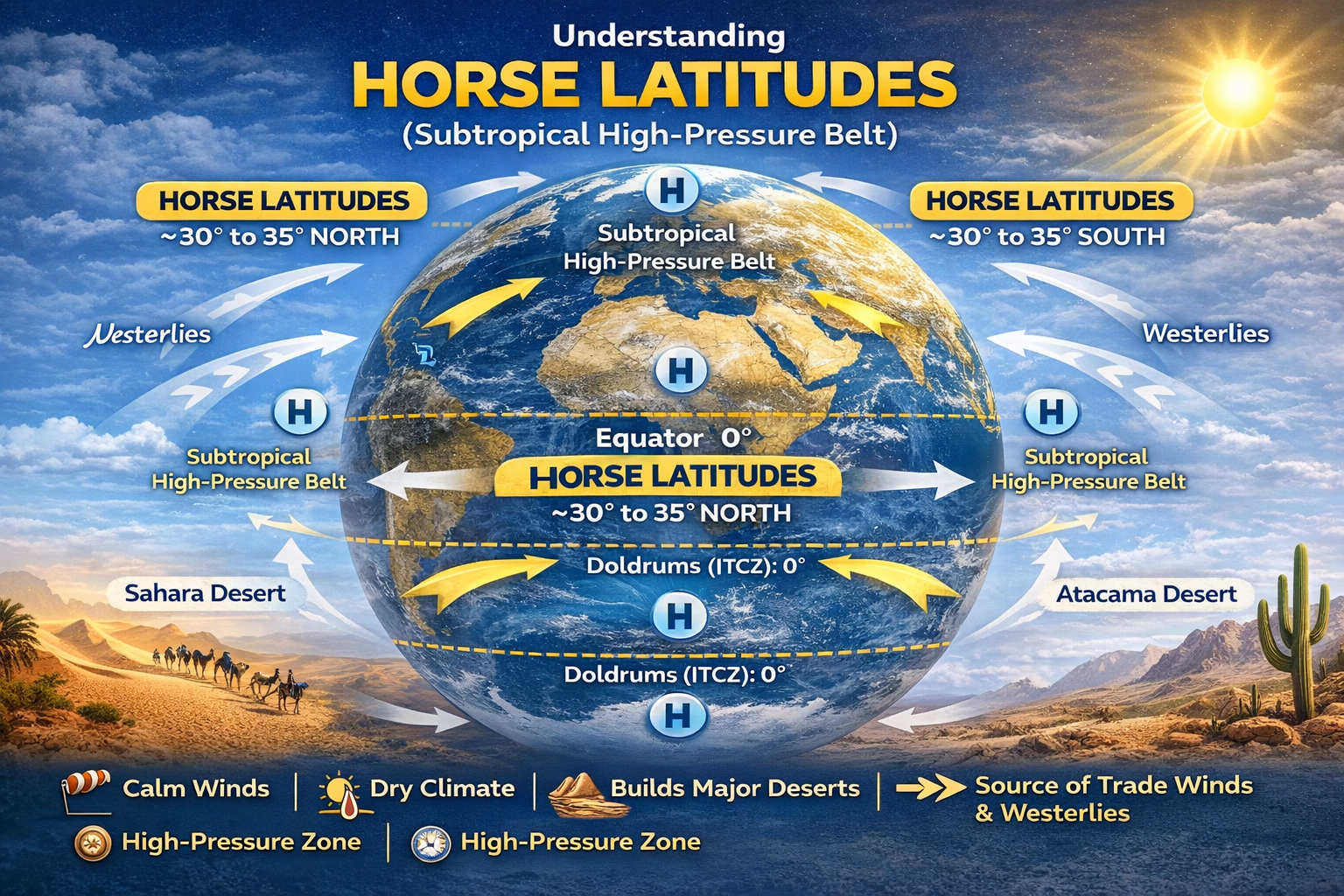
The Horse Latitudes are one of the most significant and intriguing components of Earth’s global atmospheric circulation system. Known for calm winds, high pressure, and dry climatic conditions, these latitudes have played a crucial role in shaping global climate patterns, desert formation, ocean currents, and historical maritime navigation.
Thank you for reading this post, don’t forget to subscribe!This blog explains what Horse Latitudes are, why they are called so, their causes, and their geographical importance in a comprehensive and reader-friendly manner.
What Are Horse Latitudes? (Definition)
In geography, Horse Latitudes refer to the subtropical belts of high atmospheric pressure located approximately between 30°–35° North and 30°–35° South latitudes.
Key Characteristics
- High atmospheric pressure
- Descending air currents
- Clear skies
- Weak or calm surface winds
- Hot and dry climatic conditions
These regions mark the transition zone between tropical and temperate wind systems.
Why Are They Called “Horse Latitudes”?
The term “Horse Latitudes” has a strong historical and maritime origin.
Most Accepted Explanation
During the 15th–18th centuries, sailing ships transporting horses from Europe to the Americas often became stranded in these calm high-pressure zones due to lack of wind. As supplies dwindled, sailors were forced to throw horses overboard to conserve drinking water.
This tragic but historically significant practice gave rise to the name “Horse Latitudes.”
Other Theories (Less Accepted)
- The term may derive from the Spanish word “horno” (meaning heat), referring to hot conditions.
The maritime explanation remains the most widely accepted in geography.
Location of Horse Latitudes
Horse Latitudes are found:
- Around 30°–35° North (Northern Hemisphere)
- Around 30°–35° South (Southern Hemisphere)
They form a continuous belt across:
- Atlantic Ocean
- Pacific Ocean
- Indian Ocean
- Adjacent continental regions
Causes of Horse Latitudes
Horse Latitudes are formed due to global atmospheric circulation, especially the Hadley Cell.
1. Descending Air from the Hadley Cell
- Warm air rises at the Equator (Doldrums/ITCZ).
- This air moves poleward at higher altitudes.
- Around 30° latitude, the air cools and sinks, creating high pressure.
2. Adiabatic Heating
- As air descends, it compresses and warms.
- This reduces relative humidity and prevents cloud formation.
3. Weak Pressure Gradient
- High pressure dominates, resulting in light and variable winds.
Climatic Features of Horse Latitudes
| Feature | Description |
| Pressure | High pressure |
| Winds | Calm or light |
| Rainfall | Very low |
| Sky | Clear and cloudless |
| Temperature | Hot summers, mild winters |
Geographic Importance of Horse Latitudes
Horse Latitudes play a vital role in Earth’s physical and human geography.
1. Birthplace of the World’s Major Deserts
Most of the world’s hot deserts lie near Horse Latitudes, such as:
- Sahara Desert
- Arabian Desert
- Kalahari Desert
- Atacama Desert
- Australian Desert
➡ Descending dry air suppresses rainfall, leading to arid conditions.
2. Source of Major Wind Systems
Horse Latitudes act as the origin region for:
- Trade Winds (blow toward the Equator)
- Westerlies (blow toward higher latitudes)
Thus, they are central to the global wind circulation system.
3. Influence on Ocean Currents
Persistent high pressure and wind patterns help shape:
- Subtropical ocean gyres
- Warm and cold ocean currents
This affects marine climate, fisheries, and coastal weather.
4. Impact on Human Settlement and Agriculture
- Low rainfall limits agriculture.
- Irrigation-dependent farming dominates.
- Sparse population density in many regions.
- Nomadic pastoralism common historically.
5. Historical Importance in Navigation
- Sailing ships often faced delays due to calm winds.
- Influenced trade routes and colonial maritime strategies.
- Led to major innovations in navigation and ship design.
6. Climatic Stability
Horse Latitudes contribute to:
- Climatic stability in subtropical regions
- Clear skies favourable for solar energy generation
- Predictable weather conditions for observatories and space research facilities
Horse Latitudes and Climate Change
With global warming:
- Subtropical high-pressure belts may expand poleward.
- Deserts may expand into semi-arid regions.
- Increased drought risk in many countries.
Understanding Horse Latitudes is therefore critical in climate change studies and environmental planning.
Difference Between Doldrums and Horse Latitudes
| Aspect | Doldrums | Horse Latitudes |
| Latitude | Around Equator | Around 30° N & S |
| Pressure | Low | High |
| Air Movement | Rising air | Descending air |
| Rainfall | Heavy | Very low |
| Climate | Hot & humid | Hot & dry |
Conclusion
The Horse Latitudes are a cornerstone of Earth’s atmospheric circulation system. Their calm winds, high pressure, and dry conditions have shaped deserts, wind belts, ocean currents, human history, and global climate patterns. The term itself reflects a powerful historical connection between geography and human experience.
A clear understanding of Horse Latitudes not only strengthens geographical knowledge but also helps us interpret climatic change, environmental challenges, and global weather systems more accurately.
Leave a Reply