Introduction: India’s Resilience Under Pressure
Thank you for reading this post, don’t forget to subscribe!India stands at a critical economic juncture. In August 2025, U.S. President Donald Trump announced steep tariffs—up to 50%—on a wide range of Indian exports. This move directly impacts industries worth over $35 billion annually, including gems and jewellery, textiles, carpets, shrimp, and machinery.
While analysts estimate these tariffs could shave 0.4–0.8 percentage points off India’s GDP growth if prolonged, the nation’s diverse economic base, robust domestic consumption, and proactive trade diversification strategies offer a path to resilience.
This blog explores how India can still grow between 2025 and 2030, which sectors are vulnerable, which sectors are primed for growth, and where investors should focus for strong returns.
1. The Tariff Shock: Immediate Impact on Key Sectors
1.1 Sectors Facing the Biggest Headwinds
According to CRISIL and Morgan Stanley, the following sectors are most exposed to U.S. tariff hikes:
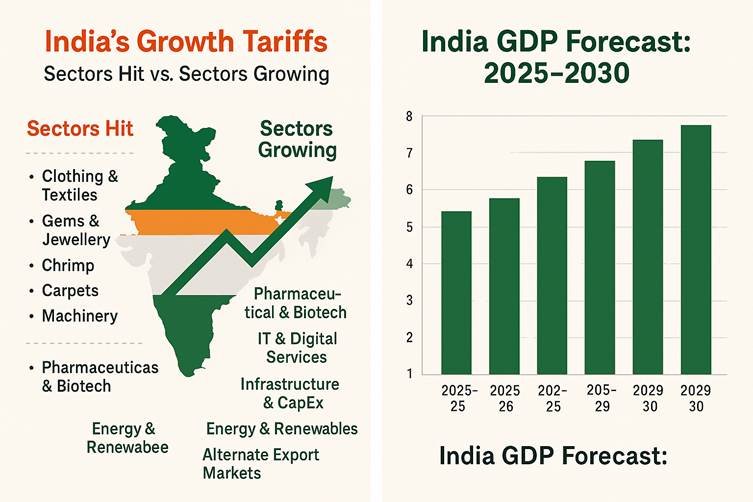
- Textiles & Apparel – The U.S. is India’s largest market for cotton garments, denim, and home textiles. A 50% tariff severely erodes competitiveness.
- Gems & Jewellery – Especially polished diamonds and gold jewellery, which account for billions in exports annually.
- Seafood (Shrimp) – India is the world’s largest exporter of frozen shrimp to the U.S.; tariffs will likely shift demand to competitors like Vietnam and Ecuador.
- Carpets & Floor Coverings – High-end handwoven carpets from Uttar Pradesh and Kashmir may lose market share.
- Machinery & Light Engineering Goods – Small and medium engineering exporters face reduced margins.
2. India’s Strategic Pivot: Turning Crisis into Opportunity
Despite the tariff shock, India is far from defenceless. The government is leveraging three major strategies to sustain growth.
2.1 Trade Diversification
- Expanding exports to Europe, Middle East, Africa, ASEAN.
- Strengthening trade pacts with UAE, Australia, and the UK.
- Targeting emerging African markets where Indian goods have strong demand.
2.2 Make in India & Atmanirbhar Bharat
- Boosting domestic manufacturing to replace imports and encourage exports to tariff-free markets.
- Large-scale investments in electronics, defence equipment, and rail manufacturing.
2.3 Infrastructure & Capital Expenditure Push
- Record spending on railways, highways, airports, and renewable energy.
- Infrastructure pipeline worth over ₹10 lakh crore planned for 2025–2030.
3. Growth Forecast: 2025–2030
3.1 GDP Projections
Even with tariffs:
- 2025–26: 6.1–6.5% GDP growth (down from 7% pre-tariff forecast)
- 2027–2030: Potential rebound to 6.8–7.2% if diversification succeeds.
3.2 Key Growth Drivers
- Domestic Consumption – Rising middle class, urbanisation, and increased disposable incomes.
- Digital Economy – Expansion of fintech, e-commerce, and AI-based services.
- Energy Transition – Solar, wind, green hydrogen investments.
4. Investment Hotspots: Sectors Set to Outperform
If you’re an investor looking for 5-year growth potential, here are the top picks:
4.1 Pharmaceuticals & Biotech
- India is the pharmacy of the world, supplying affordable generics and vaccines.
- U.S. tariffs haven’t targeted pharma yet, and global demand is rising.
- Investment idea: Large-cap pharma and biotech innovators.
4.2 Information Technology & Digital Services
- Global enterprises continue to rely on India’s IT giants for cloud, AI, and cybersecurity.
- While some U.S. client budgets may tighten, the AI-driven transformation is a huge long-term opportunity.
- Investment idea: large and Mid-cap IT firms with AI verticals.
4.3 Infrastructure & Capital Goods
- Government-backed mega projects ensure steady demand for cement, steel, engineering services.
- Investment idea: Infra construction and cement majors.
4.4 Renewable Energy & Electric Mobility
- India targets 500 GW of renewable capacity by 2030.
- EV adoption is accelerating with FAME-II incentives.
- Investment idea: green energy, power, and Electric Vehicles companies.
4.5 Consumer Staples & FMCG
- Domestic demand will be relatively immune to tariff shocks.
- Investment idea: Consumer and FMCG major companies.
5. Sectors to Approach with Caution
- Export-heavy apparel without diversified markets.
- Gem & jewellery companies relying on U.S. orders.
- Small-cap seafood exporters without processing plant upgrades.
- Non-diversified engineering SMEs.
6. Investor Strategy for the Next 5 Years
6.1 Diversify Across Resilient Sectors
Avoid over-concentration in tariff-hit industries. Balance portfolios with domestic demand-driven sectors.
6.2 Focus on Government-Backed Themes
Infrastructure, energy transition, and manufacturing localisation will have policy tailwinds.
6.3 Global Exposure Through Indian Multinationals
Invest in companies with strong overseas market presence beyond the U.S.
Conclusion: Adaptability Will Define India’s Next Growth Phase
While Trump’s tariffs present a clear challenge, they also act as a catalyst for economic diversification, domestic capacity building, and strategic trade expansion. India’s strong fundamentals—robust consumption, growing digital economy, and infrastructure boom—remain intact.
For investors, the next 5 years will reward those who can identify sectors insulated from tariff shocks and positioned to leverage government reforms and global trends.

Leave a Reply